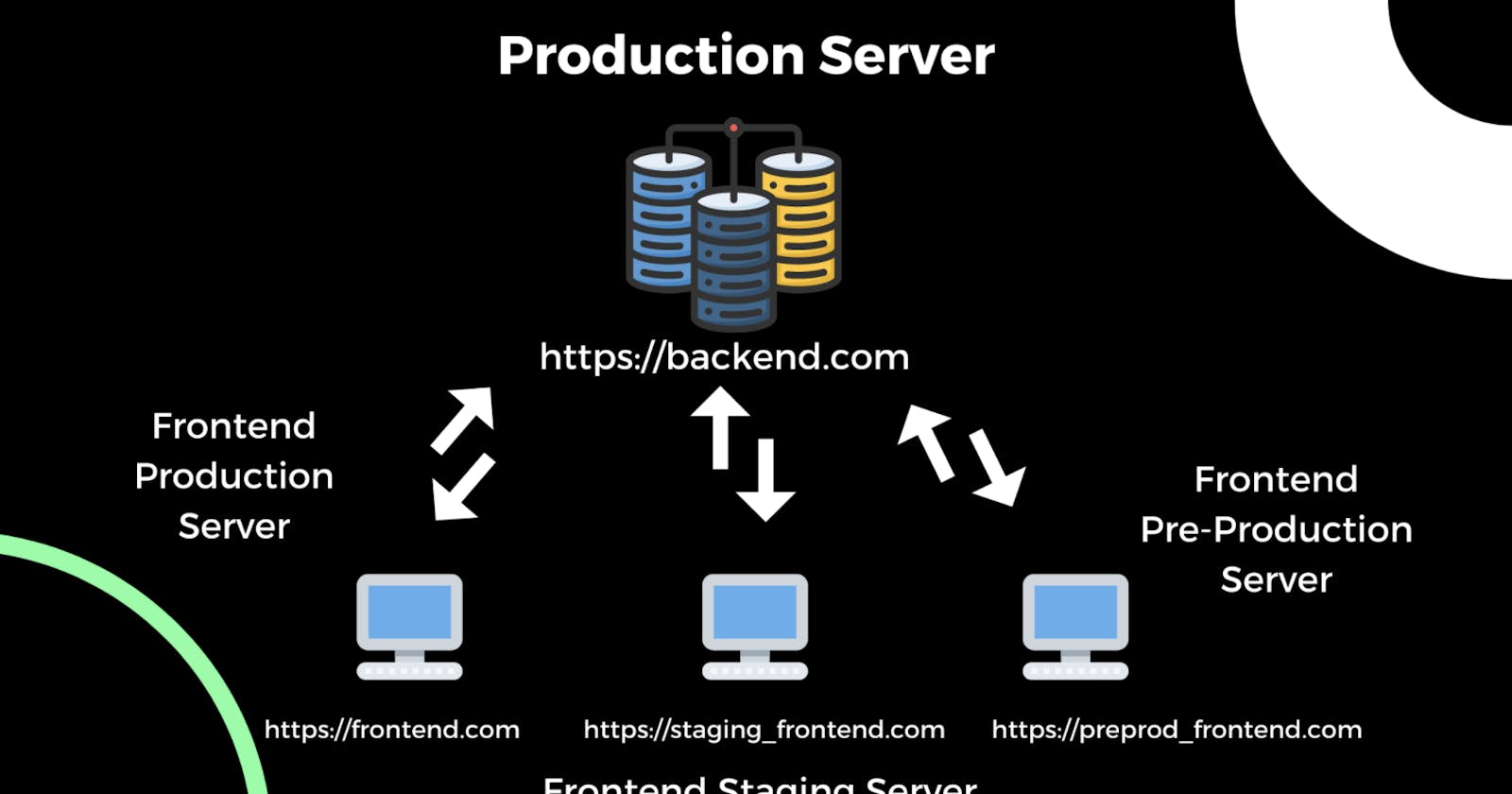
CORS stands for Cross-Origin Resource Sharing, and it is a mechanism used by web browsers to allow web pages to make requests to a different domain than the one the page originated from.
In general, web browsers have a same-origin policy, which means that web pages can only access resources from the same domain as the page itself. This policy is in place to prevent malicious websites from accessing sensitive data from other domains. However, this can sometimes create problems for legitimate use cases where web pages need to make requests to other domains, such as when using APIs or accessing resources from a content delivery network (CDN).
CORS provides a way for web servers to explicitly grant permission to web pages to access resources from other domains. When a web page makes a request to a different domain, the browser sends an HTTP request that includes an "Origin" header with the domain of the page. The server can then respond with a set of headers that indicate which domains are allowed to access the resource, and which HTTP methods (e.g. GET, POST) are allowed.
By using CORS, web developers can create more powerful and flexible web applications that can access resources from multiple domains while still maintaining security and preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data.